
Arthrosis of the ankle joint — degenerative-dystrophic damage to cartilage tissue. But because when the disease progresses, the articular surface of the bone is involved in the process, it is more accurate to call it osteoarthritis. In foreign literature, when describing this disease, the term osteoarthritis is used, which indicates not only degenerative changes, but inflammation against this background.
Osteoarthritis — This is a progressive chronic joint disease in which cartilage, articular surfaces of bones, capsules and periarticular tissues are destroyed. This leads to pain and impaired joint movement. Ankles rarely develop osteoarthritis, unlike knees. This disease occurs more often in women over 50 years of age and in athletes with leg injuries. For arthrosis of the ankle joint, treatment depends on the manifestation of the disease and is selected individually by an orthopedic traumatologist. Doctors use methods that have proven their effectiveness and safety, and adopt a multidisciplinary approach to treat problems and prevent the development of joint pathology.
This article is advisory in nature. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist after consultation.
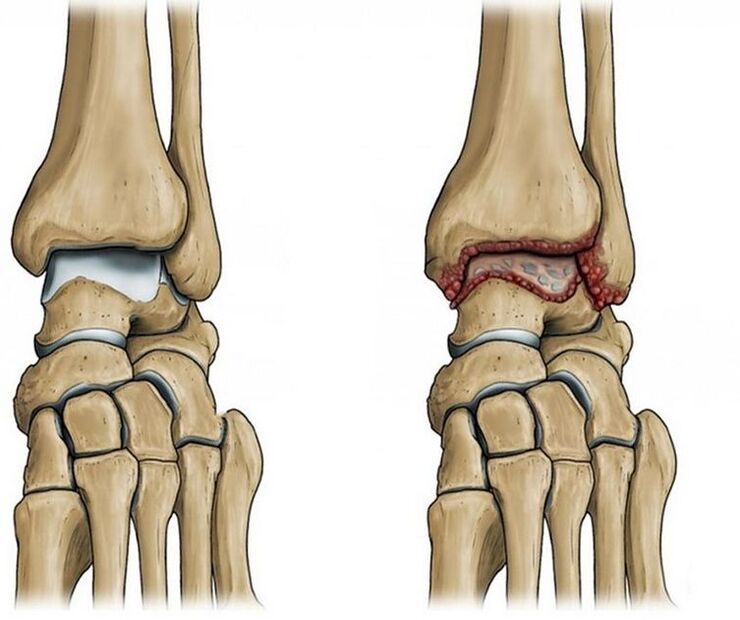
How the disease develops
The ankle joint is formed by three bones: tibia, fibula and talus, covered by an articular capsule and strengthened by ligaments. Thanks to the work of the muscles, the legs are bent and extended. Normally, the articular surfaces are smooth and easily slide relative to each other during movement. Covered with dense, elastic cartilage, its main function — bone protection and load absorption. The joint cavity contains synovial fluid. It plays the role of intra-articular lubrication, preventing the friction of joint elements and their abrasion during movement.
But as a result of injury or natural aging of the joint, the articular surface becomes rough, and the cartilage tissue loses its smoothness and elasticity. When the cartilage is damaged and when degenerative changes develop, the bones begin to touch each other when moving in the joint, which is accompanied by pain.
In an attempt to "defend" and to compensate for further damage to the joint and surrounding tissues, osteophytes are formed — growths along the edges of the articular surface of bones. As a result, joint mobility is partially or even completely limited.
Depending on the main cause, the following types of osteoarthritis are distinguished:
- Primary or idiopathic osteoarthritis. In this case we are talking about degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joints
- Secondary is associated with exposure to a specific causative factor, usually a previous joint injury. And this form is most often diagnosed
Predisposing factors
The main predisposing factors for the development of arthrosis of the ankle joint:
- intra and periarticular injuries, such as fractures, tears and ligament ruptures
- ankle surgery
- inflammatory joint lesions in the past
- intense loads: professional sports, ballet, long walks, work related to long periods of "standing"
- sedentary lifestyle
- wearing high heels for a long time
- overweight
- Hereditary collagenopathy leading to impaired collagen synthesis
- chronic injury to the joint structure due to excessive load
- metabolic disorders: diabetes, gout
- Estrogen deficiency in menopausal women
- rheumatic disease
- foot deformities, such as flat feet
- degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine, complicated by the formation of intervertebral hernia, which is accompanied by compression of the nerve roots
Ankle arthrosis: symptoms
The main sign of arthrosis — Pain is what makes you seek help from a doctor. At the beginning of the development of the disease, the pain is bothersome only after prolonged exercise and decreases with rest.
Depending on the degree of pathological changes in the joints, the pain becomes more intense and persistent at rest and even at night. Other symptoms occur.
There are three stages of the disease:
- The first stage is characterized by slight swelling, redness of the skin of the joint area, pain in the afternoon or after intense exercise. Unpleasant sensations are localized along the front surface of the foot, along the joint line and move to the lateral surface of the ankle. X-rays of the feet may not yet show any changes.
- In the second stage, the pain becomes constant, dryness appears when moving the joint, mobility is limited, and the joint "jams. "When examined on x-ray, growth along the edges of the articular surface of the bones is noticeable: tibia, ankle and talus, as well as narrowing of the spacejoints
- In the third stage, the joint is deformed, which is why only rocking, low-amplitude movements are possible. Radiographs reveal massive bone growth, the joint space is sharply narrowed or even absent. Due to the instability of the joint, patients often twist their legs, which only worsens the situation due to sprains, ligament tears and deterioration of the general condition
Pain with ankle arthrosis has characteristic features:
- The maximum is expressed at the beginning of the movement — the so-called initial pain
- Increases significantly with load, especially when running, jumping
- It usually appears in the evening, at night or right after waking up
Due to the pain, there is limited movement in the legs, as well as congestion in the joints as the cartilage is destroyed.
Symptoms appear in waves: exacerbations alternate with remissions. With exacerbations, symptoms are more pronounced. During remission, symptoms gradually subside and may disappear altogether.
Which doctor should I contact?
If pain and stiffness in ankle movements occur, you should consult an orthopedic traumatologist. If other causes of joint discomfort are identified, consultation with a neurologist, rheumatologist or endocrinologist may be necessary.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor explains the complaint, determines how long the pain has been observed, which contributes to its appearance and intensification. Specialists collect data on existing diseases, injuries and lifestyle characteristics, conduct examinations, assess range of motion in joints and perform diagnostic tests.
Already based on the information received, it is possible to make a diagnosis, but to confirm it and draw up a competent treatment plan, additional examination methods are required, which may include:
- X-ray of the ankle joint, which is of primary importance in making a diagnosis and determining the stage of development of the disease. The image shows narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes on the edge of the articular surface of the bone, cysts and signs of bone thinning located under the cartilage.
- A CT scan of the joint reflects the picture in more detail. Doctors can assess in detail the state of the patient's bone structure and cartilage tissue
- MRI is used to study cartilage and soft tissue
- Joint ultrasound to assess the condition of the soft joint structure
Treatment of arthrosis
Pathological treatment is long-term and is carried out under the supervision of an orthopedic traumatologist on an outpatient basis. How to cure foot arthrosis depends on the level of damage and existing complications.
The main goal of treating diseases in modern clinics is to relieve leg pain, improve the patient's quality of life and slow the progression of arthrosis. To do this, doctors develop a set of therapeutic and preventive measures, medical and non-medical, and also adjust the patient's lifestyle.
Lifestyle and nutrition correction
Adequate physical activity and nutritional correction will help curb degenerative changes. After the examination, the clinic doctor can give recommendations on weight loss, as well as optimizing the load on the legs.
Drug treatment
Medicines are selected individually, based on examination data, symptoms, and concomitant diseases. Patients can be prescribed:
- Analgesic. Most often these are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, gels, injections to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Antidepressants and anticonvulsants for prolonged, severe, intractable pain
Exercise therapy
Specially selected exercises help maintain range of motion in the joint, reduce pain, and curb the development of degenerative changes. The patient performs the recommended exercises at first under the supervision of a specialist, and then — on his own, at home.
massage
Lower limb massage normalizes joint tissue nutrition. It is prescribed beyond the acute stage. During the session, the specialist performs passive movements on the joints, which prevent muscle shortening and joint stiffness.
Assistive devices
Orthoses, crutches and special walkers may be recommended to relieve pressure and stabilize the ankle joint.
Surgery
It is used only in cases of severe destruction of articular cartilage and limited joint mobility. After surgery there is a long recovery period and conservative treatment. Endoprosthetics or arthroplasty at the final stages of the development of ankle arthrosis — arguably the only chance to avoid deformity and maintain joint mobility.
Why is ankle arthrosis dangerous?
Changes that have already formed in the joint cannot be restored. Therefore, treatment aims to slow down the pathological process to maintain the patient's ability to work and quality of life. It is possible to achieve these goals only with timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor's recommendations.
When arthrosis develops, a clear deformation of the joint is formed. The range of movement is sharply reduced, as a result, the ability to support the legs becomes difficult; walking without crutches or crutches is almost impossible.
Chronic and persistent pain in the joints leads to anxiety and depressive disorders.
Prevention
Prevention of arthrosis includes the following measures:
- Avoid traumatic activities. For example, jumping from a great height, running
- Avoid injury
- Be careful in icy conditions, wear non-slip shoes
- Control your weight
- Normalizing body weight will help reduce stress on the ankle joint
- Stay moderately active
- A sedentary lifestyle is dangerous and leads to complications, as well as overload and microtraumas
- Keep your joints healthy
- Seek medical advice immediately and treat musculoskeletal disorders
Key points from the article:
- The prevalence of degenerative-dystrophic disease in the leg joints is 87%
- Occupational hazards, daily habits, and past injuries can cause arthrosis of the ankle joint.
- Common symptoms of arthrosis — pain, which is accompanied by a throbbing sound when moving, local swelling, and then limited movement of the legs
- Treatment of ankle arthrosis is often conservative and includes medical and non-medical methods.
- Progression of ankle arthrosis leads to disability and complete loss of foot function























